Water Bottle,Crystal Water Bottle,Custom Water Bottle,Custom Glass Water Bottle XUZHOU NORTH STAR PACKING PRODUCTS CO.,LTD , https://www.nspglassbottle.com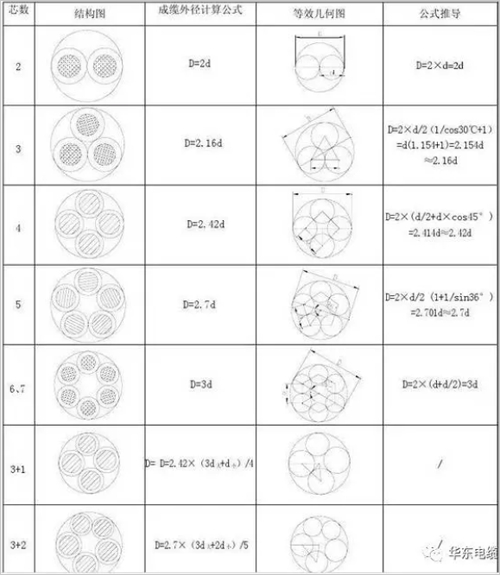
Watt-shaped wire core cable calculation formula:
Two-section circular insulated core wire cable outer diameter: D=2d
Three-section circular insulated core wire cable outer diameter: D = 2.154d
Four-section circular insulated core wire cable outer diameter: D=2.414d
Five-section circular insulated core wire cable outer diameter: D=2.7d
3+1 (main line is fan-shaped), its cable outer diameter approximation formula D=2.31h
4 cores (for fan shape), the approximate outer diameter of the cable is D=2.2h
3 cores (for fan shape), the approximate outer diameter of the cable is D=2.11h
3+2, 4+1 (main line is tile-shaped), the approximate outer diameter of the cable is D=2h+d (outer diameter of the core)
Three big one small circle: D = (3 * d large + d small) * 0.61
Four big one small circle: D = (4 * d large + d small) * 0.54
Three large two small tiles, four big one small tile shape: D = 2.1547 * h watt high + d small
The calculation formula for the selection of the cable-connected parallel mode:
1. The formula for calculating the selection of the circular core and the wire mold:
12 equal core D=2d
23 equal core D=2.16d
34 equal core D=2.42d
45 equal core D=2.7d
56 (7) isometric D = 3d
63*1 core D=2.4 (3d large + d small) / 4
73+2 core D=2.7 (3d large +2d small)/5
84+1 core D=2.7 (4d big + d small)/5
2. Formula for calculating the selection of the fan-shaped core and cable and the linear mode:
12 equal core D=2d
23 equal core D=2.16d
33+1 core D=2.31 (3d large + d small) / 4
44 equal core D=2.31d
55 equal core D=2.42d
64+1 core D=2.42 (4d big +d small)/5
73+2 core D=2.42 (3d large +2d small)/5
For example: YJV 3×240+2×120 240 core fan height 21mm, 120 wire core 15.2mm, then the theoretical outer diameter of our cable is 2.42×(3×21+2×15.2)÷5=45.2, we will A 45mm or 46mm mold can be used.
Note: Above D represents the outer diameter of the cable, and d represents the diameter of the circular core or the height of the sector. In order to facilitate the quick and accurate selection of the parallel mode when cabling, this calculation method is for reference.
Calculation formula and derivation of the outer diameter of the multi-core cable circular insulated core
Set the outer diameter of the insulated core to d, and the outer diameter of the cable to be D. The formula for calculating the outer diameter of the cable is as follows:
Cable diameter calculation formula
Three big one small circle: D = (3 * d large + d small) * 0.61
Four big one small circle: D = (4 * d large + d small) * 0.54
Three large one small round, four big one small round: D = 2.1547 * h watt high + d small
Five big one small formula D = 0.5 * (5D big + D small)
The calculation of the cable outer diameter of the "three big two small" core structure is usually based on the method of checking the graphical curve table, but the calculation accuracy is difficult to guarantee. In particular, it is very inconvenient to use "spreadsheets" for structural calculations. Although the rapid calculation of the "three big two small" core structure cable outer diameter, whether using the chart method, or the empirical formula, can give the correct results, but using the Mathcad software calculation method, and the "spreadsheet" software for structural size Compared with the calculation, you can get twice the result with half the effort.
Attachment: 24 easy-to-understand wire and cable knowledge points
1. The twisting pitch is the distance along the axial direction when a certain component of the cable rotates in a spiral shape.
2. The twist-in ratio refers to the ratio of the difference between the actual length of a single wire and the length of the strand pitch in a pitch and the length of the pitch.
3. The process parameters affecting the cross-sectional area of ​​the fan-shaped stranded conductor are single wire number, single wire diameter, twisted pitch, and sector height.
4. The nominal cross section is an approximate cross section used to represent the series specifications.
5. The change of the pitch of the wire conductor is achieved by changing the twisted cage or pulling the master and slave gears.
6. Extrusion is the process of continuously and uniformly encapsulating a plastic mixture into a conductor or cable core.
7. Shielding is a shielding layer that limits the electric field magnetic field within the cable or cable components and protects the cable from external electric and magnetic fields.
8. The main factors affecting the quality of extrusion are
1) the quality of the plastic itself (ie the quality of the raw materials);
2) the performance of the extruder;
3) extrusion temperature;
4) Retracting line tension;
5) host and traction speed;
6) The device after the core wire preheating plastic extrusion - the mold (the geometrical structure design and size of the mold, the temperature, the pressure, etc.)
9. The winding process mainly has
1) Cable core diameter D (diameter of the core before wrapping);
2) wrapping the angle of the package;
3) wrapping pitch;
4) wrapping gap;
5) wrapping tape width
10. The main factors affecting the insulation eccentricity of the insulated core of J45 extruder are
1) The wire is not smooth or elliptical;
2) the core is too large;
3) The position of the core and the mold sleeve is not adjusted;
4) The core to the exit distance is too short
11. The possible causes of breakdown of wire and cable are
1) The dielectric strength of the insulating raw material itself does not meet the product requirements;
2) The insulating layer contains impurities and bubbles;
3) Wire and cable insulation eccentric;
4) mechanical damage insulation;
5) The surface of the conductor has burrs, broken ends, etc.
12. Insulation resistance and volume resistivity Conceptually, insulation resistance describes the insulation properties of an insulation structure, such as the insulation resistance of wires per kilometer; volume resistivity describes the degree of insulation material, that is, the difference in insulation characteristics.
13. The outer sheath process inspection project has
1) jacket material;
2) average thickness;
3) the thinnest point thickness;
4) the cross section of the sheath;
5) Power frequency spark test;
6) Appearance mark;
7) appearance;
8) Cable outer diameter and f value
14.f value is the difference between the largest and smallest diameters measured on the same section of a cable or cable perpendicular to the axis.
15. The thinnest point thickness is the minimum thickness of any cross section of a component of the cable.
16. Sampling test is a test conducted by a manufacturer to extract a complete wire and cable according to the manufacturing lot and cut the sample or component from it.
17. Cable inspection of insulated core quality mainly
1) The wire size and structure of the insulated core;
2) Whether the insulation thickness and outer diameter dimensions conform to the standard;
3) Whether the insulation color or print number conforms to the standard.
4) Check product identification and inspection status identification
18. Pay attention when using power frequency spark machine
1) The electrode box housing of the spark machine should be grounded;
2) Both ends of the test electrode should be grounded to protect the electrode;
3) Safety protection interlocking device to ensure that the high voltage power supply is automatically disconnected when the test electrode is turned on;
4) Check the safety protection interlocking device before use, the signal bell must be able to operate normally;
5) Operate the spark machine. When the output voltage is zero, close the electrode box and start it. The test voltage is gradually increased to the rated value.
6) The conductive core or shield of the tested wire shall be grounded reliably. If there is breakdown, reset it in time;
7) Periodically check the stability sensitivity of the output voltage of the spark machine, etc.
19. Conductors, Insulators, and Semiconductors: An object with a high electrical conductivity is called a conductor. Any object that cannot conduct electricity is called an insulator. Conductive properties between the conductor and the insulation are called semiconductors.
20. The superconductor is a current flowing in the conductor. Due to the existence of the resistance of the conductor itself, heat is generated in the conductor to cause loss, thereby limiting the ability of conducting. When some conductors are below a certain temperature, their own resistance will completely disappear. We call such metal conductors superconductors.
21. Resistance: The resistance that a current flows when flowing inside a conductor is called resistance.
22. Batch refers to the number of unit products included in the batch; sample size refers to the number of sample units included in the sample
23, pitch diameter ratio: pitch diameter ratio theoretical aspect ratio and practical pitch ratio, the so-called pitch diameter ratio is the ratio of pitch (pitch) to diameter, if this diameter is the pitch circle diameter, the result is the theoretical section The diameter ratio, if calculated using the strand diameter, results in a practical pitch ratio. When understanding the theoretical aspect ratio, pay attention to a feeling, that is, the festival circle! The pitch circle is the track of the center of the conductor in the same stranded layer. It is called the pitch circle, and its diameter is the pitch circle diameter! Is the pitch diameter = stranded outer diameter - conductor diameter (provided that the single conductor diameter of the stranded conductor is equal)
24. Stranding coefficient: refers to the ratio of the actual length of the twisted single wire to the length of the strand pitch in a twisted pitch. The twist-in ratio: refers to the ratio of the difference between the actual length of the twisted single wire and the length of the twisted joint and the twisted pitch in a twisted pitch!