Titanium Dioxide R223,Titanium Oxide Rutile,Titanium Dioxide Rutile Price,Rutile Titanium Dioxide Tio2 Wuxi Qijun New Material Co., LTD , https://www.tio2supplier.com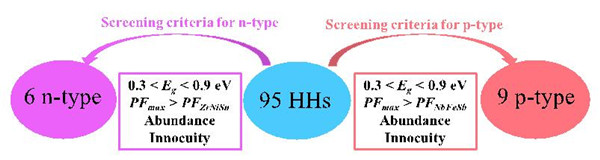
[ Instrument Network Instrument Development ] Recently, Zhang Yongsheng, a researcher at the Solid State Institute, has made new progress in high-throughput screening of high-performance half-Heusler (HH) alloy thermoelectric materials. Relevant research provides theoretical guidance for subsequent experiments. Understanding the physical mechanism of thermoelectric performance provides an idea. The relevant research results are published in the Journal of Physical Chemistry C.
Thermoelectric materials can convert temperature difference into electrical energy, which has important application value in mitigating energy crisis. The thermoelectric conversion efficiency of materials is usually characterized by thermoelectric figure ZT. HH materials are widely concerned by the thermoelectric materials industry due to their excellent electrical properties, mechanical properties, thermal stability and rich mineral resources. At present, p-type NbFeSb and n-type ZrNiSn are more studied, but their high thermal conductivity hinders the increase of ZT value. Therefore, finding a parent HH material with high thermoelectric properties has become a top priority. However, there are still a large number of HH systems whose thermoelectric properties have not been studied, and the existing high-throughput work generally adopts a simpler model approximation. Therefore, a more accurate method is used to search for efficient HH matrix materials and explore behind them. The physical mechanism is important.
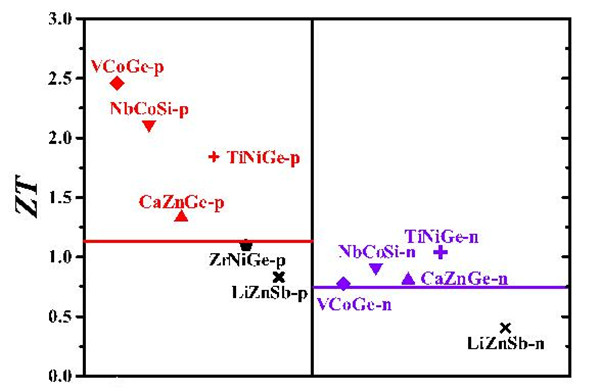
To this end, Zhang Yongsheng's research team used the metamorphic potential theory to search for 95 HH compounds with high throughput. Considering the factors of band gap, mineral deposit and non-toxicity, nine p-type and six n-type HH candidate systems were finally screened, and their electrical properties (power factor) were better than those of NbFeSb and ZrNiSn materials. It is found through research that its excellent electrical properties are due to the high energy band degeneracy contributing to the Seebeck coefficient, and the low deformation potential, light band and high group velocity synergistically contribute to its high conductivity. In addition, two compounds (LiZnSb and CaZnGe) were found to have lower lattice thermal conductivity (less than 4 W m-1 K-1 at 300 K) due to their strong non-harmonic lattice vibration. It is found by calculation that the thermoelectric figure of HH compound is mainly dominated by electrical properties. VCoGe, NbCoSi and TiNiGe are good candidates for thermoelectric materials due to their high power factor and relatively low thermal conductivity.
This work not only provides a good candidate system for experiments, but also provides ideas for understanding the physical mechanism of thermoelectric performance.
The above research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Hefei Sub-center of the Chinese Academy of Sciences Supercomputing Center and the Suzhou New Materials Supercomputing Center.
Figure 1. Flow chart of a high-throughput search for a better p(n)-type parent HH candidate material than NbFeSb (ZrNiSn).
Figure 2. ZT values ​​for theoretically calculated HH candidate materials at 900 K. The red and purple lines represent the theoretical calculations of the ZT values ​​of p-type NbFeSb and n-type ZrNiSn, respectively.